Gaussian Filter:
The Gaussian filter is a linear filter that is usually used as a smoother . The output of the gaussian filter at the moment is the weighted mean of the input values, and the weights are defined by formula
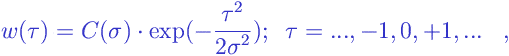 |
where
is the “distance” in time from the current moment;
is the parameter of the Gaussian filter;
is the normalization constant chosen to make the sum of all weights equal to the unit value.
If you plot the values of against
, then the plot coincides with the famous bell-like curve describing the density of the gaussian distribution . This explains the word “gaussian” in the name of the filter.
The gaussian filter is completely defined by a single parameter . The greater the value of
, the wider the window function
, and, hence, the greater the degree of smoothing.
The gaussian filter provides better suppression of higher frequencies than the rectangular filter and the triangular filter .
Besides the one-dimensional gaussian filter described above, there are extensions to the case of two dimensions, say, . Such two-dimensional gaussian filters are widely used in image processing .
